If you make them laugh, will you make them buy?
Can humor sell? What an interesting question and not without some serious implications. Many marketing experts have pondered over this question for over a hundred years.
Claude C Hopkins, one of the early founders of modern advertising and author of "Scientific Advertising" in the early 19th century famously said “People don’t buy from clowns”. But that was 100 years ago and we have learned quite a bit more about consumer behavior since then.
There's quite a lot of evidence now that suggests that entertianing and likeable ads work better.
- Rory Sutherland, Vice Chairman, Ogilvy UK
Intuitively, we know it's probably not a good idea to use humor for selling businesses such as life insurance, funeral services etc. What else can we say about products & services that may or may not sell with humor?
Are there specific vectors such that if a product or service lies on that vector, we use humor else we use something else? How about high value products? or products that require a lot of consideration? Luxury products? Lifestyle products like apparel, appliances etc.? What about FMCG?
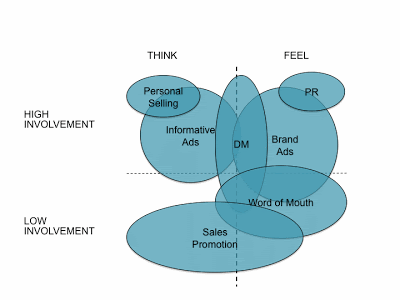
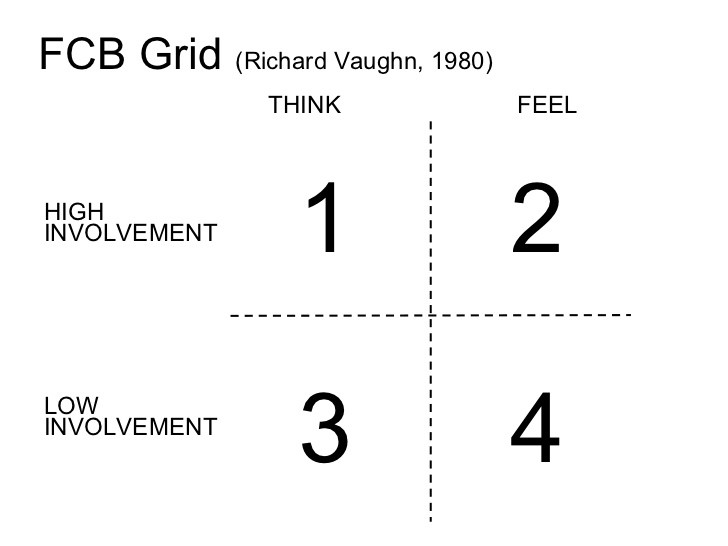
In 1980, Richard Vaughn, SVP of a leading ad agency FCB (Foote, Cone & Belding) introduced a framework called FCB Grid. It's a 2x2 grid that divides consumer purchasing decisions into four quadrants based on two dimensions:
-
1. Involvement - (high vs. low)
-
2. Thinking vs. feeling (rational vs. emotional)
Since then, the FCB grid has become a popular product-classification scheme in advertising and consumer research. It's used by marketers as a strategic guideline for determining advertising campaign messages. As a marketing model, it helps advertisers create effective advertising strategies by classifying consumer purchasing behavior.
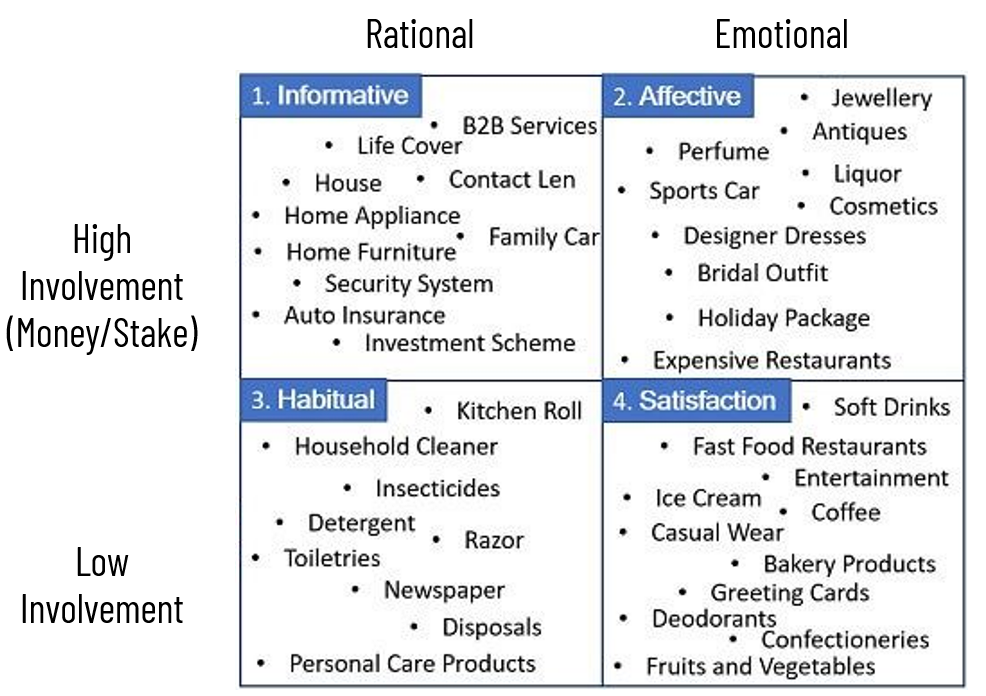
4 Quadrants of FCB Grid
- Q1 – Informative: These products are generally of of high value, purchased once or twice in a lifetime and require a lot of thinking & buyer involvement. Examples - real estate, life insurance, car, investments, security system, etc.
- Q2 – Affective: These products are high value, but their purchase decision is more influenced by the buyer’s emotions, rather than analytical thinking. Examples - bridal dress, jewellery, cosmetics, antiques, perfumes, etc.
- Q3 – Habitual: Regular use products such as a household cleaner, gasoline, detergent, newspaper and many more are stated as habitual products.
- Q4 – Satisfaction: Impulse purchase products such as ice creams, confectioneries, fast food, soft drinks, casual clothes, entertainment and greeting cards. These products bring satisfaction to the consumers.
Marketing Strategies for 4 Quadrants of FCB Grid
Most SME marketers design and run marketing campaigns based on their gut feel and choose channels like SEO, SEM, social etc. or outreach strategies such brand awareness, PR etc. based on what they see everybody else doing (without much strategic marketing decision making). As a marketer, if you can accurately plot your product or service on the FCB Grid and guide your marketing strategy accordingly, your chances of success are 10x higher than other marketers who are flying blind.